
The difference v^īetween the observed value £^ and any arbitrarily assumed (or One wants to regard the "residuals as variables" the
Practice, one often hears talks about "minimized residuals", The observed valueĪ given sample, the residuals can be computed in one way only. Should be noted that a residual, as defined above,Ī uniquely determined value and not a variable. With inverted signs are usually called corrections. The symbol will indicate the sample mean to make the notation We have seen, we are not able to compute the unknown value I 'orĪccordinace with the basic postulate of the error-theory, will
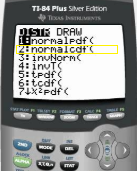
#How to use normal cdf pdf
The transformed sample that has a Gaussian PDF is:Īn argument t obtained from equation (4-13) To the basic postulate of the error-theory we can say that:Īnd c^ are respectively the mean and the standard deviation of theīe used for the required transformations as follows: The variance S of the given sample as follows: Sample in such a way that the transformed Variance S^ of its corresponding sample of random errors Indicates that the variance S^ of the sample L is Value of the mean y^ of the parent PDF of £. Instance, to determine the probability P (x In order to be able to use the tables of the standard normalĬDF for computations concerning a given normal random variable X, we first have to standardize X, I.E. Van der Waerden, b.L., 1969: Mathematical Statistics, Springer-Verlag.Areas under the standard normal curve from 0 to t.Is not as straightforward, as it is in the parametric case (section 6.4.6).For the adjustment, the above model is reformulated as:.In this section we are going to deal with the adjustment of the linear model (6.68), I.E.It can be regarded as the variance of unit If we develop the quadratic form V pv 3) considering the observations l to be influenced by random errors only, we get an estimate к for the assumed factor к given by.This means that we have to work with the weight matrix к£- 1 We know the relative variances and covariances of the observations only. 6.4.7 Variance-Covariance Matrix of the Parametric Adjustment Solution Vector, Variance Factor and Weight Coefficient Matrix.In this case, the observation equations will be The system of normal equations (6.76) has a solution X.In which we neglect the higher order terms.
#How to use normal cdf series

3.3.6 Mean and Variance-Covariance Matrix of a Multisample The mean of a multisample (3.48) is defined as.It is not difficult to see that the variance-covariance matrix can also be written in terms of the mathematical expectation as follows:.

On the other hand, the r-th central moment of the pdf is given by:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
